The bodies of the thoracic vertebrae are larger than those of cervical vertebrae (Picture 1).
The characteristic feature for a typical midthoracic vertebra is the spinous process, which is long and has a pronounced downward angle that causes it to overlap the next inferior vertebra. The superior articular processes of thoracic vertebrae face anteriorly and the inferior processes face posteriorly. These orientations are important determinants for the type and range of movements available to the thoracic region of the vertebral column.
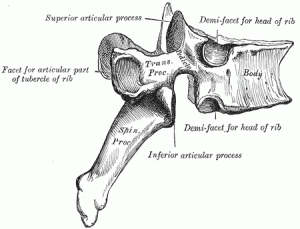
Thoracic vertebrae have several additional articulation sites, each of which is called a facet, where a rib is attached. Most thoracic vertebrae have two facets located on the lateral sides of the body, each of which is called a costal facet (costal = “rib”). These are for articulation with the head (end) of a rib. An additional facet is located on the transverse process for articulation with the tubercle of a rib.
Detailed description
The thoracic vertebrae are intermediate in size between those of the cervical and lumbar regions; they increase in size from above downward, the upper vertebrae being much smaller than those in the lower part of the region. They are distinguished by the presence of facets on the sides of the bodies for articulation with the heads of the ribs, and facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercles of the ribs.
The bodies in the middle of the thoracic region are heart-shaped, and as broad in the antero-posterior as in the transverse direction. At the ends of the thoracic region they resemble respectively those of the cervical and lumbar vertebrae. They are slightly thicker behind than in front, flat above and below, convex from side to side in front, deeply concave behind, and slightly constricted laterally and in front. They present, on either side, two costal demi-facets, one above, near the root of the pedicle, the other below, in front of the inferior vertebral notch; these are covered with cartilage in the fresh state, and, when the vertebrae are articulated with one another, form, with the intervening intervertebral fibrocartilages, oval surfaces for the reception of the heads of the ribs.
The pedicles are directed backward and slightly upward, and the inferior vertebral notches are of large size, and deeper than in any other region of the vertebral column.
The laminae are broad, thick, and imbricated—that is to say, they overlap those of subjacent vertebrae like tiles on a roof.
The vertebral foramen is small, and of a circular form.
The spinous process is long, triangular on coronal section, directed obliquely downward, and ends in a tuberculated extremity. These processes overlap from the fifth to the eighth, but are less oblique in direction above and below.
The superior articular processes are thin plates of bone projecting upward from the junctions of the pedicles and laminae; their articular facets are practically flat, and are directed backward and a little lateralward and upward.
The inferior articular processes are fused to a considerable extent with the laminae, and project but slightly beyond their lower borders; their facets are directed forward and a little medialward and downward.
The transverse processes arise from the arch behind the superior articular processes and pedicles; they are thick, strong, and of considerable length, directed obliquely backward and lateralward, and each ends in a clubbed extremity, on the front of which is a small, concave surface, for articulation with the tubercle of a rib.
The first, ninth, tenth, eleventh, and twelfth thoracic vertebrae present certain peculiarities, and must be specially considered (Picture 2).