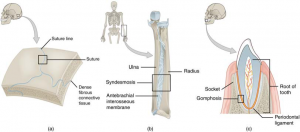
At a fibrous joint, the adjacent bones are directly connected to each other by fibrous connective tissue, and thus the bones do not have a joint cavity between them (Picture 1). The gap between the bones may be narrow or wide. There are three types of fibrous joints:
- A suture is the narrow fibrous joint found between most bones of the skull.
- At a syndesmosis joint, the bones are more widely separated but are held together by a narrow band of fibrous connective tissue called a ligament or a wide sheet of connective tissue called an interosseous membrane. This type of fibrous joint is found between the shaft regions of the long bones in the forearm and in the leg.
- Lastly, a gomphosis is the narrow fibrous joint between the roots of a tooth and the bony socket in the jaw into which the tooth fits.